CFO GROUP INTEGRATED SERVICES
Latest 2025 Step-by-Step Guide: Who Needs to Pay Income Tax Singapore
CFO Group • July 15, 2025
If you’re wondering who needs to pay income tax in Singapore, the answer depends on your annual income, your tax residency status, and the type of income earned. Generally, if your total income is above S$22,000 in a calendar year, you must file an income tax return. Whether you actually pay tax depends on your chargeable income, allowable deductions, and eligible tax reliefs.
This guide explains how personal income tax works, covering residents, foreign employees, self-employed individuals, and those earning rental income, business income, or foreign-sourced income.
Key Takeaways
- Tax residents (Singapore citizens, Singapore permanent residents, or foreigners meeting the 183-day rule) generally enjoy progressive income tax rates, reliefs, and deductions.
- If your gross income exceeds S$22,000, you must file income tax return.
- Non-resident individuals face different tax treatment, often paying a flat withholding tax rate on employment income or other income.
- Foreign-sourced income is generally not taxable in Singapore unless specific conditions apply under the Income Tax Act or double taxation agreements.
Tax Residency and Tax Purposes in Singapore
| Category | Criteria | Tax Treatment / Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Residents | • Singapore citizen or permanent resident who ordinarily resides in Singapore • Foreigner who stayed/worked ≥183 days in a calendar year (temporary absences count) • Foreign employees with an employment period of ≥183 days | • Progressive personal income tax rates (0%–24%) • Eligible for tax reliefs and allowable deductions • May qualify for No Filing Service via Auto-Inclusion Scheme |
| Non-Resident Individuals | • Stayed or worked <183 days in Singapore in a calendar year | • Employment income taxed at 15% or resident rates (whichever is higher) • Other income (director’s fees, consultancy, etc.) subject to withholding tax rate • No personal reliefs allowed |
Under the legal framework of the Companies Act, the company directors decide who can appoint company secretary—it is the board. The decision is documented in minutes of board meetings (or by written resolution) and retained with company records. Many companies use a registered filing agent (acting through a registered qualified individual) to submit officer changes to the regulatory authorities promptly.
Income Threshold, Year of Assessment, and Filing Requirements
You must file a tax return if your total income (including employment income, rental income, and business income) exceeds S$22,000 in the year of assessment (YA).
Filing process:
- E-file via myTax Portal (deadline: 18 April).
- Paper filing is also available (deadline: 15 April).
- Payments can be made via internet banking or GIRO.
Note: Your gross tax payable is calculated after applying tax reliefs and deductions. You only pay income tax on your chargeable income, not your full gross income.
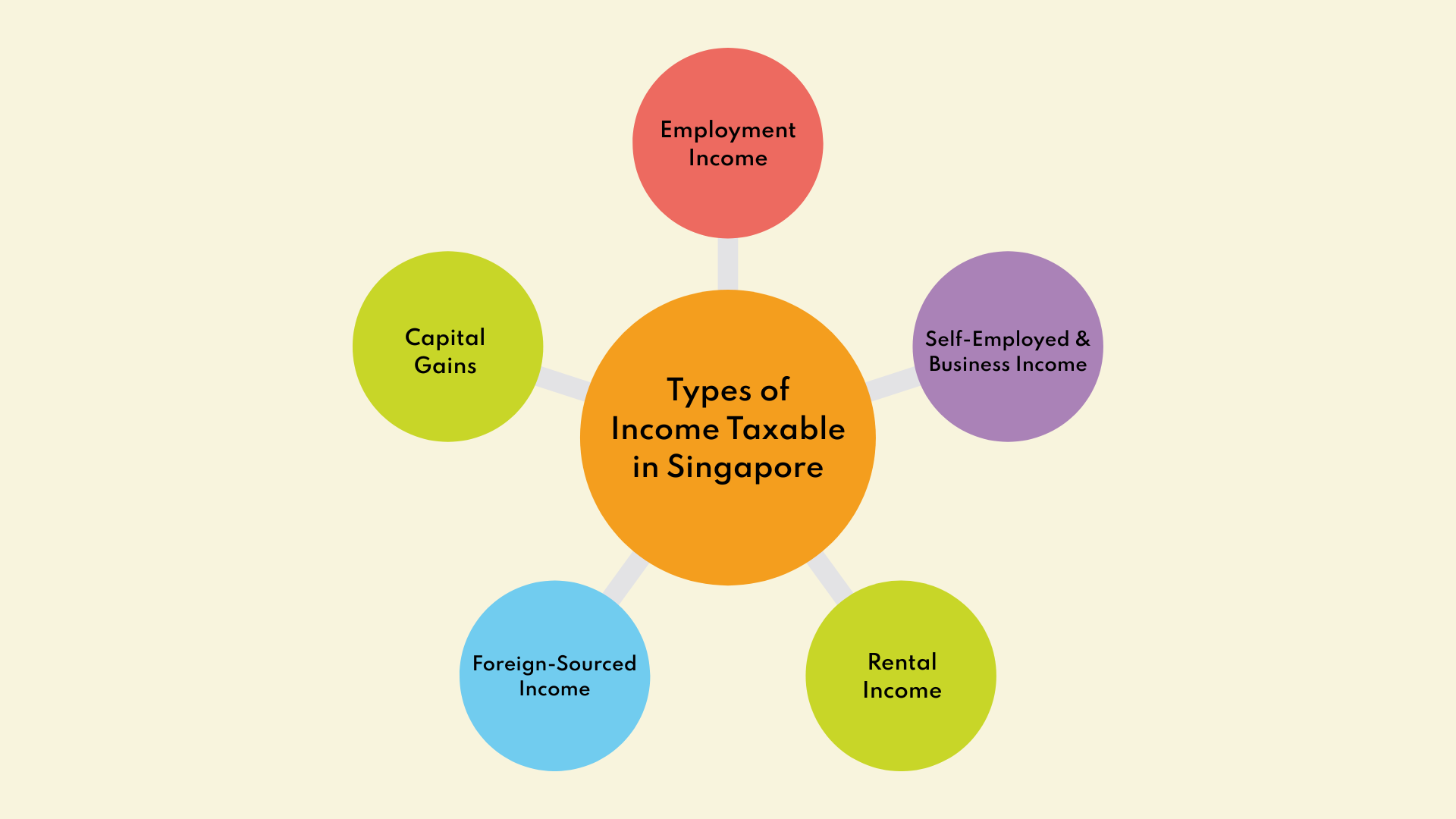
Types of Income Taxable in Singapore
Employment Income
- Salaries, bonuses, allowances, stock options, and benefits from Singapore employment are income taxable.
- Foreign employees working for a foreign employer but seconded to Singapore are still taxed on income derived here.
Self-Employed Individuals and Business Income
- Profits from any trade, business, profession or vocation (including freelance and gig work) are trade income.
- You must prepare income details (profit & loss, balance sheet) and track net profit.
- Even if your net income is below the filing threshold, IRAS may require you to file for tax purposes.
Rental Income
- Rental income from property in Singapore is taxable. You can claim allowable deductions (repairs, mortgage interest, property tax).
Foreign-Sourced Income
- Generally tax exempt for individuals.
- Exceptions: If received via a foreign country partnership or deemed taxable under double tax treaties.
- Double taxation agreements (DTAs) prevent paying tax twice on the same income.
Capital Gains
- Capital gains (e.g., sale of shares, personal property, or lottery winnings) are not subject to personal income tax under the Income Tax Act.
Tax Reliefs, Allowable Deductions, and Tax Savings
Singapore offers many eligible tax reliefs to lower chargeable income:
- CPF contributions
- NSman relief
- Parent/child reliefs
- Course fee relief
These create opportunities for tax savings, reducing your final tax liability.
Filing Process for Income Tax Return
- Year of assessment (YA) runs on a calendar year basis.
- E-filing opens on 1 March; deadline 18 April.
- Auto-Inclusion Scheme pre-fills your employment income details if your employer participates.
- No Filing Service: If notified by IRAS, you may not need to file tax return unless your circumstances change.
Penalties for Non-Compliance and Unpaid Tax
Failing to file or pay results in late payment penalties and fines:
- Incorrect return (no intent): Penalty up to 200% of unpaid tax, fine up to S$5,000, and/or 3 years’ jail.
- Tax evasion (wilful intent): Penalty up to 400% of unpaid tax, fine up to S$50,000, and/or 5 years’ jail.
Ensuring timely tax filing safeguards against higher tax bills and enforcement.
Summary
Understanding tax in Singapore means knowing when to file income tax return, what counts as taxable income, and how your residency status affects tax treatment.
- Tax residents enjoy progressive rates, deductions, and reliefs.
- Non-residents face flat withholding taxes and fewer benefits.
- Self-employed individuals must track business income and net profit.
- Rental income and employment income are taxable, while capital gains are exempt.
- Double taxation agreements protect against paying twice on the same income.
By staying compliant, declaring income derived in Singapore, and maximizing tax reliefs, you can reduce your final tax and avoid unpaid tax penalties.
Corporate Income Tax Made Simple with CFO Group
CFO Group makes corporate income tax simple, accurate, and stress-free. From preparing detailed financial statements to ensuring compliance with Singapore’s Income Tax Act, our team helps companies navigate every step of the corporate income tax return process. We optimize allowable deductions, identify eligible tax reliefs, and structure your accounts for maximum tax savings, while ensuring timely submissions to IRAS for every year of assessment. Whether you’re a local SME, a multinational with overseas employment ties, or facing complex issues like double taxation agreements, CFO Group provides end-to-end support so you avoid penalties, reduce your tax liability, and focus on growing your business with confidence.